Java iterator pattern example 2017-01-16 01:02
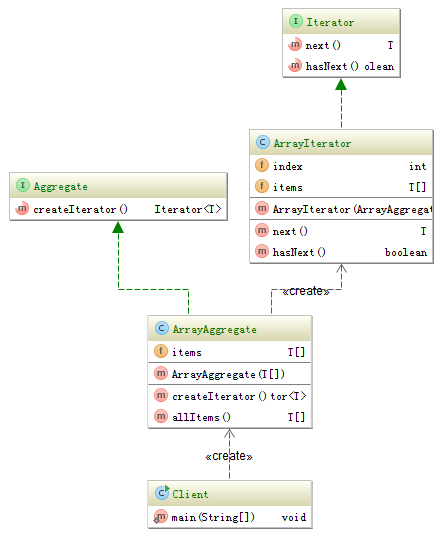
The best example of iterator pattern are source code of util package in JDK. If you want to learn more, I recommend you read the source code of JDK. (Including but not limited to:Iterator, ArrayList and HashMap). In this page I will make an easy example to show how iterator works. The structure of classes is like following.
Aggregate and ArrayAggregate are like following.
public interface Aggregate<T> {
Iterator<T> createIterator();
}
public class ArrayAggregate<T> implements Aggregate<T> {
private T[] items;
public ArrayAggregate(T[] items) {
this.items = items;
}
@Override
public Iterator<T> createIterator() {
return new ArrayIterator<>(this);
}
public T[] allItems() {
return items;
}
}
To make it clear I don't put iterator into ArrayAggregate. You can move the implement of iterator into aggregate like JDK does.
public interface Iterator<T> {
T next();
boolean hasNext();
}
public class ArrayIterator<T> implements Iterator<T> {
private int index;
private T[] items;
public ArrayIterator(ArrayAggregate<T> tArrayAggregate) {
items = tArrayAggregate.allItems();
}
@Override
public T next() {
return items[index++];
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return index <= items.length - 1;
}
}
Use iterator like following.
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayAggregate<Integer> arrayAggregate = new ArrayAggregate<>(new Integer[]{1, 2, 3});
Iterator<Integer> iterator = arrayAggregate.createIterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
}
The key of iterator pattern is "Provide a way to access the elements of an aggregate object sequentially without exposing its underlying representation."