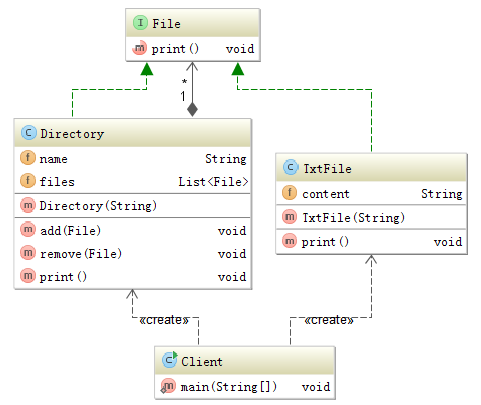
Java composite pattern example 2017-01-03 00:37
Composite pattern is used to handle a group of objects in the same way. Let's say we have two different kinds of File. The one is TxtFile and the other one is Directory. In composite pattern we treat them as File in the same way. The code is like following.
public interface File {
void print();
}
public class TxtFile implements File {
private String content;
public TxtFile(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
@Override
public void print() {
System.out.println(content);
}
}
public class Directory implements File {
private String name;
private List<File> files = new ArrayList<>();
public Directory(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void add(File file) {
files.add(file);
}
public void remove(File file) {
files.remove(file);
}
@Override
public void print() {
System.out.println("directory " + this.name + ":");
for (File file : files) {
file.print();
}
}
}
Both TxtFile and Directory implement the print method of the interface. You can call print method without if statements. Treat them as File and call print method, TxtFile will print the content of it and Directory will iterate all TxtFile and print the content of them one by one.
The client code is like following.
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file1 = new TxtFile("file1");
File file2 = new TxtFile("file2");
File file3 = new TxtFile("file3");
File file4 = new TxtFile("file4");
Directory directory1 = new Directory("directory1");
Directory directory2 = new Directory("directory2");
directory1.add(file1);
directory1.add(file2);
directory2.add(file3);
directory2.add(file4);
directory1.add(directory2);
directory1.print();
}
}
We can add TxtFile or Directory into a Directory and handle them in the same way. The output of client is like following.
directory directory1:
file1
file2
directory directory2:
file3
file4